Flower EncyclopediaENTER THE WORLD OF FLOWERS |
Other News
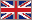
Crocus sativus
Category: Bulbs and tubers
05 Apr : 14:47
To view pictures click on them
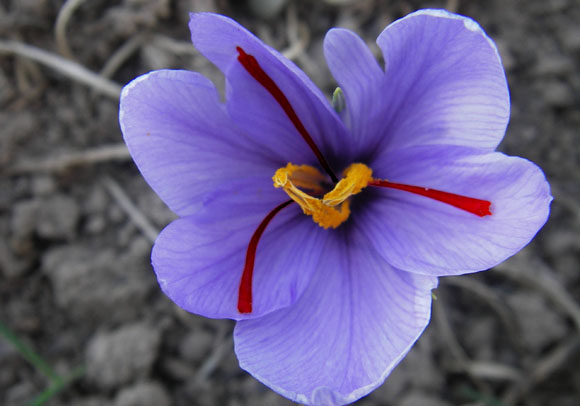






 Saffron crocus (Crocus sativus) is a cultural form of the family Iridaceae Crocus (Iridaceae). The three stigmas of the flower (the distal ends of pistils - the female reproductive organs of the plant) and part of his neck (a stalk connecting stigmas to the rest of the plant) is dried and used in cooking as a spice and dye.
Saffron crocus (Crocus sativus) is a cultural form of the family Iridaceae Crocus (Iridaceae). The three stigmas of the flower (the distal ends of pistils - the female reproductive organs of the plant) and part of his neck (a stalk connecting stigmas to the rest of the plant) is dried and used in cooking as a spice and dye.Saffron, which has for decades been the most expensive spice in the world by weight, is native to Southwest Asia. Cultivated for the first time in the region of Greece.
Its colors are purple color and shape of a star. Dissolve during the night. Its delicate flowers are hand picked and dried stigmas. We need more than 150 000 plants to obtain 1 kg of saffron, which makes it the most expensive spice in the world. Rather only ¼ teaspoon saffron is enough to give flavor and aroma of the dish for 6 people.
The word saffron comes from the Old French term of 12 century "safran", which comes from the Latin "safranum". "Safranum" is also linked with the Italian "zafferano" and Spanish "azafrán". "Safranum" comes from the Arabic word "asfar", which means "yellow" by paronimnoto "za'faran", the name of the spice in Arabic.
History:
The history of saffron cultivation reaches back more than 3000 years in the past. The wild ancestor of rabbits saffron crocus is a kind of autumn crocus - Crocus cartwrightianus. Nurture it people bred wild specimens otbirayki those with unusually long stigmas. Thus, a sterile mutant form of C. cartwrightianus, C. sativus was created in the late Bronze Age Crete. Experts believe saffron was first documented in an Assyrian botanical guide of 7 th century BC, established during the reign of Ashurbanipal. Documentation is available for the use of saffron to treat about 90 diseases in the period of 4000 years. Saffron is used as a spice and medicine in the Mediterranean since then, the use and cultivation slowly spread to other parts of Eurasia and to North Africa and North America. Prezposlednite decades saffron cultivation reaches and Oceania.
Ancient Greece and Rome.
Minoytsite saffron are depicted in the palace frescoes around 1500-1600 BC, presenting its use as medicine. Later Greek legends tell of sea voyages to Cilicia. There travelers hoping to gain what they thought was most valuable saffron in the world. Another legend tells of Crocus and Smilaks - how the Crocus is bewitched and transformed into the original saffron crocus. Ancient Mediterranean peoples-including perfumers in Egypt, physicians in Gaza, townspeople in Rhodes and the Greek hetaerae courtesans-used saffron in their perfumes, ointments, putpuri, makeup, sacrifices and treatments.
In the late Hellenistic Egypt, Cleopatra used saffron in bathing to deliver greater pleasure during love-making. Egyptian healers used saffron to treat all types of gastrointestinal complaints. Saffron is used to dye fabrics in the Levant cities as Sidon and Tyr. The Roman scholar Cornelius Aval Tsels prescribes saffron in medicines for wounds, coughs, colic, and scabies. Romans so loved saffron that Roman colonists brought their saffron, when they settled in southern Gaul, where it was extensively cultivated until the fall of Rome in 271, the Competing theories state that saffron is returned to France only in the 8 century by the Moors or the Avignon papacy in 14 century.
Varieties:
The world are grown several varieties of saffron. Spain, a major exporter of saffron, generally produces soft varieties with less bright color, flavor and aroma. Spanish varieties are those with tradenames "Spanish Superior" and "Creme" and they are graded according to government minimum standards. Most Italian saffron is more potent in these characteristics. The bulk of the most powerful and valuable varieties in the world, however, come from Greek Macedonia, Iran and Kashmir. U.S., have banned imports of Iranian saffron, while India has banned export of high quality saffron abroad. Furthermore, in places like New Zealand, France, Switzerland, England and the United States come from various "boutique" crops. In the United States, Pennsylvania German saffron, which is famous for earth tones in the aroma and taste, is produced in relatively small quantities.
There are a few widely regarded by consumers for high quality saffron types. For example akilskiyat saffron (Italian zafferano del L'Aquila) is grown in the Abruzzo region in the valley around the town leaned. There, saffron is grown on about 8 hectares area. Currently, this is the only place in the world where it grow. It is distinguished by shape and color of the stigmas, and pistils and its content visoikoto safranal. They give an unusually sharp akilskiya saffron flavor. Furthermore, high crocin enhances many of its coloring ability. Akilskiyat saffron was brought to Italy from Spain during the Inquisition by a Dominican monk. Subsequently by the end of the Middle Ages akilskiyat saffron is one of the most sought-after varieties in Europe. But large-scale cultivation of saffron quality and quantity in Italy is in San Gavino Monreale, Sardinia. There, saffron is grown on 40 hectares (60% of Italian production). He also has very high crocin, and picrocrocin safranal. Another high-quality saffron is the Kashmiri "Mongrain" or "Lacha" (Crocus sativus Cashmirianus), beyond which India is the most expensive and hardest to find. This is because of permanent drought, disease and crop failures in Kashmir, combined with the ban on exports from India. Kashmiri saffron is known by its extremely dark maroon-purple hue, one of the darkest in the world, suggesting a strong taste, aroma and color capabilities.
Cultivation:
Conditions:
Saffron crocus grows in climates similar to Mediterranean scrub. Therefore, it grows in places like North scrub, where more than dry and semi-arid lands in the hot dry summer blow light winds. However, the plant can tolerate cold winters, capable of cold to -10 ° C and short periods of snow. If not grown in areas with high rainfall, the saffron crocus needs watering. In Kashmir, for example, average annual rainfall is 1000-1500 mm, so that Kashmiri saffron is grown without irrigation under normal rainfall. In very dry areas, where cultivated saffron crocus (for example, in Greece, where average rainfall is 500 mm, and Spain, where they are 400 millimeters), irrigation is necessary. Saffron crocus like spring rains followed by relatively dry summers. Rain falling just before flowering, however, carry higher yields. On the other hand, rain or cold weather during flowering contribute to disease. Permanent moisture and heat are also favorable for the extraction of saffron and rooting from rabbits, rats and birds. Parasites such as roundworms, leaf rust and rot bulbs also threaten the harvest.
Planting:
It is best to be planted in fields that are inclined to the south, which provides maximum sun exposure. Saffron plants need direct sunlight and do not thrive in the shade. In the Northern Hemisphere is sown in June. The bulbs are planted at a depth of 7 to 15 cm yields and quality are influenced by climate, planting depth and spacing between bulbs. Bulbs planted deeper, giving fewer flower buds and daughter corms, but the saffron is obtained with higher quality. Under the conditions existing in Italy, the planting of bulbs at 15 cm depth gives optimal saffron threads, but the shallow planting 8-10 cm gives most colors, and daughter corms. In Italy, the bulbs are planted in 2-3 cm distance. Optimal planting practices vary greatly between Italy, Greece, Morocco and Spain and are consistent with the typical climate of the country.
Another way: pre-planting and budding bloom in spring Crocus.
Winter: In sandacheta planted with plants nemrazovito and dark place. Avoid drying of the soil. After germination the light is exported. Wintering in the second year is not always successful.
Irrigation, fertilization: Sandachetata planted with small plants to keep moist until germination. After sanding begin to moderate watering and natoryava once. To prevent water retention. After pretsaftyat with root tufts are planted in the garden and fertilized again.
Category: Bulbs and tubers
Comments are turned off for this item0
| asfar iridaceae crocus sativus |
You must be logged in to make comments on this site - please log in, or if you are not registered click here to signup